Accuracy counts for so much in science. Whether a scientist is working with DNA, proteins, blood, or cell cultures, the packaging and shipping of samples impacts an entire project. Small variations in temperature, labelling, or packing not only pose the risk of wasted materials, but also have the potential to compromise years of research or invaluable clinical findings.
Here at Restore Harrow Green, we’ve learned first-hand how important stringent processes are in the handling of samples. From relocating labs on behalf of universities to helping biotech start-ups like Pureaffinity in White City, we know that biological sample storage and transportation is not just about logistics, it’s about securing the future of research.
Join us as we explore some best practices that help ensure biological materials remain viable, compliant, and secure, from initial collection through to long-term preservation and safe delivery.

Why specialist storage and transport matter
Biological samples are fragile by nature. Their integrity can be compromised by temperature fluctuations, poor handling, or delays during transit. Specialist storage and transport practices protect against degradation, contamination, and regulatory breaches. They also uphold research integrity so that experiment results remain replicable and valid. Regulatory compliance is non-negotiable, with strict standards governing laboratory specimen transport. Similarly, safety is of paramount importance, not just to laboratory personnel but also to the general public. Finally, preservation of value remains an issue since most specimens, such as patient-derived samples, are non-replaceable./
Best practices for sample collection and initial handling
Even before a sample is brought to a freezer or transportation box, how it is handled and taken determines the way things go from there. Sterile procedures are the most sensible starting point. Pipettes, containers, and personal protective equipment should all be sterilised to avoid contamination.
It is equally important to record collection details immediately. Capturing the date, time, sample type, and the name of the collector helps avoid confusion later on. Another critical step is the timely stabilisation of samples. This may involve adding preservatives or snap‑freezing, depending on the material.
Finally, separating samples by type from the outset keeps hazardous and non‑hazardous substances apart and ensures that the correct storage conditions are applied from the beginning. These practical measures reduce the risk of contaminated specimens and offer a sound foundation for maximum biological sample handling.
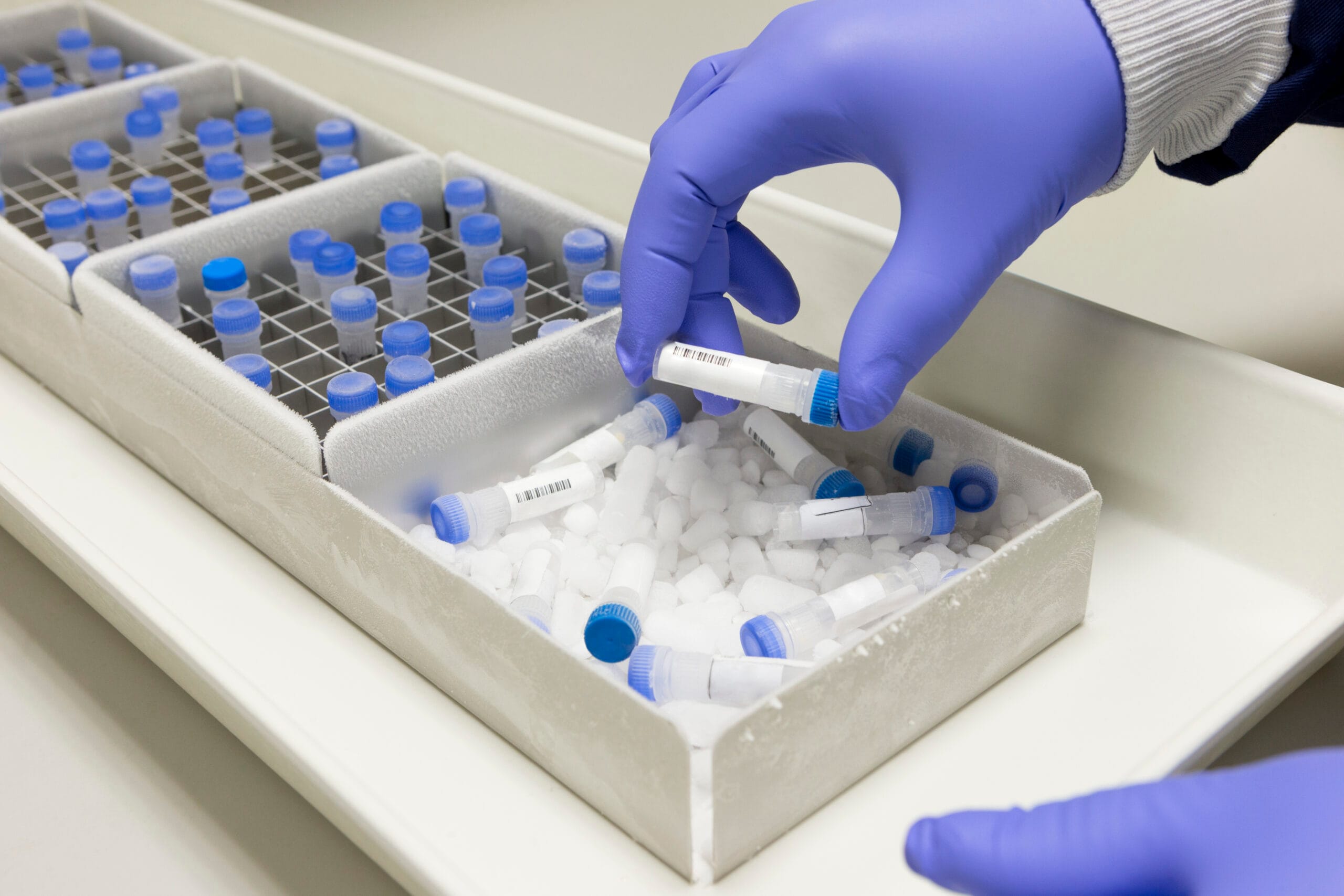
Storage conditions and organisation
Appropriate storage conditions are the bedrock of biological sample storage. The environment required is entirely based on the type of specimen:
- Ambient (15–25°C): Suitable for certain reagents and insensitive materials.
- Refrigerated (2–8°C): Suitable for short-term storage of proteins or tissue.
- Frozen (-20°C or -80°C): Suitable for long-term storage of DNA, RNA, and proteins.
- Cryogenic (-196°C in liquid nitrogen): Suitable for ultra-low temperature cryopreservation of cells and tissue.
Additional essential factors to take into consideration are:
- Humidity control to avoid degradation and condensation.
- Standby systems such as freezers and alarmed generators in the event of a power outage.
- Organisation aids, such as mapping systems and sample inventories to avoid unnecessary freeze-thaw cycles.
Our biobanking services here at Restore Harrow Green offer exactly this level of controlled environment, safeguarding samples even in the event of unexpected situations.
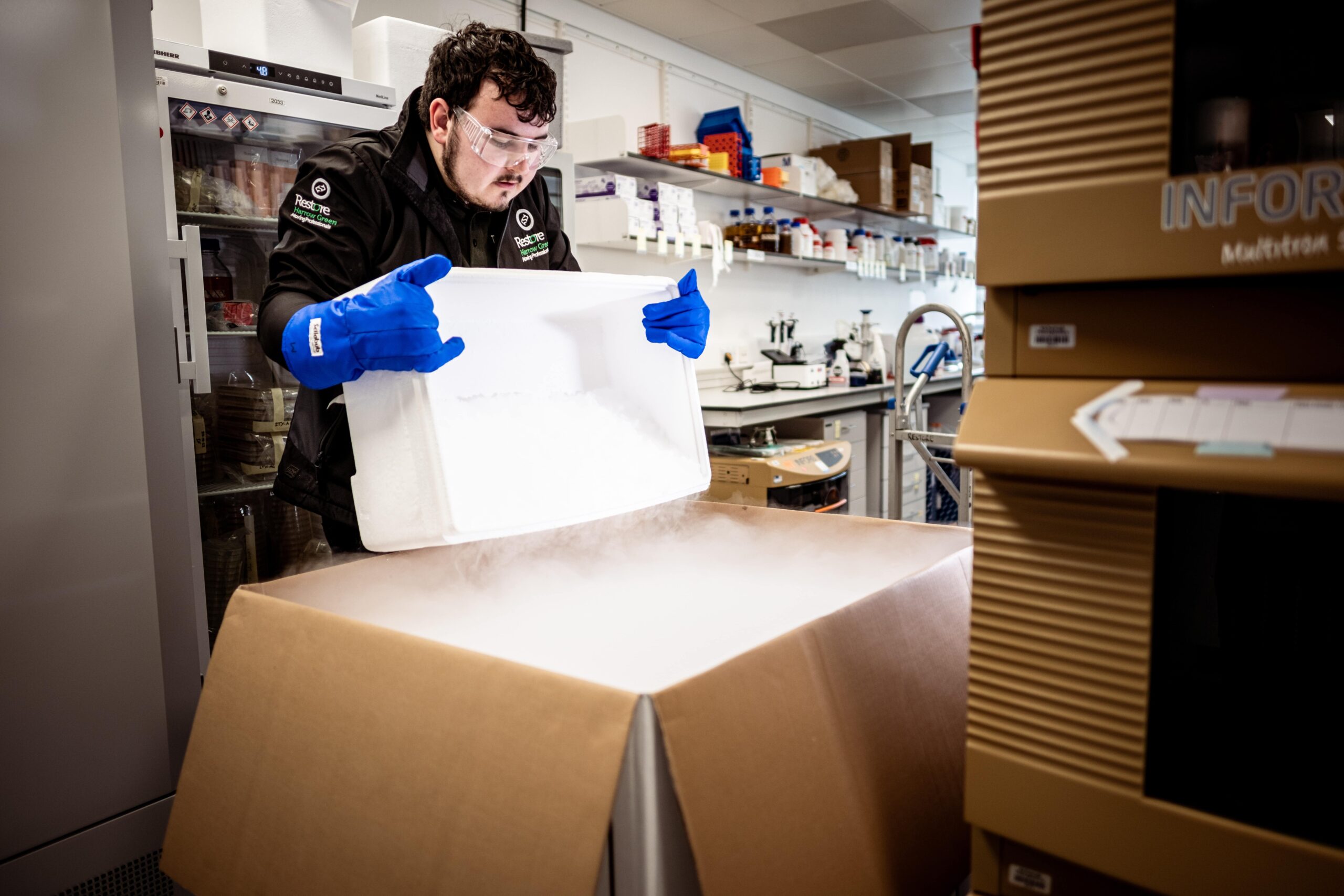
Transport is the weakest link in the chain for samples, and preparation and packaging are absolutely essential. The triple system of international acceptance remains the benchmark to beat:
- Primary container: A sealed, leak-proof tube or vial.
- Secondary container: A sealed, leak-proof bag or rigid container packed with absorbent material.
- Outer packaging: A rigid, insulating box to protect against shocks and temperature fluctuations.
Ideally, best practice also includes:
- Temperature monitoring with calibrated data loggers.
- Shock absorption by cushioning materials within packages.
- Full documentation, like permits, customs documentation, and full contact details of all parties interested.
Taken together, these steps create a protective cocoon for any specimen along its journey.

Temperature control in transit is probably the largest hurdle facing specimen transport. The risk of deviation is high during local delivery within a city or on an international flight. The most effective ways of limiting those risks are by preplanning routes and choosing the fastest carriers. Some have found that it is better to ship earlier in the week to prevent weekend hold-ups.
Increasingly, laboratories and their suppliers are putting live monitoring systems in place that track GPS location and internal temperature in real time. Another useful practice is preparing the receiving team and storage equipment in advance. When staff are ready to accept and place specimens directly into controlled environments on arrival, transfer times are reduced and sample integrity is better protected. All these combined work together for efficient specimen transport solutions that make materials viable from the point of origin to the point of destination.

Legislation on the transportation of biological samples also includes paperwork as much as packaging. Compliance with standards such as IATA Packing Instructions 650 that cover infectious materials and diagnostic samples is required. Within the European Union, ADR regulations covering the highway transport of hazardous goods must also be complied with. Laboratories must further ensure that GxP records are maintained, thus rendering each handling and storage stage traceable. Accurate and detailed documentation does more than satisfy regulators, it provides researchers with confidence that their samples have been handled appropriately.
At Restore Harrow Green, we embed these requirements into every project. Our approach is supported by dedicated services such as our biobanking facilities, which ensure controlled storage environments, and our expertise in laboratory relocations, where compliance and documentation are critical. By combining regulatory adherence with careful planning, we ensure every sample remains safe, traceable, and auditable.

Behind each successful biological material transport is a well-trained and competent team. Staff must understand blood sample transportation guidelines and be able to apply them with confidence.
They need thorough knowledge of PPE use and biosafety procedures that reduce exposure risks. Training should also prepare them to respond calmly and correctly in the event of incidents such as container breaches.
Managing temperature excursions is another crucial skill. Teams must recognise when corrective actions are appropriate and when a sample can no longer be considered viable.
Finally, safe disposal practices must be ingrained so that hazardous biological materials are never mishandled. At Restore Harrow Green, our laboratory relocation experts and ADR-certified drivers receive ongoing training to ensure they remain aligned with evolving requirements in biological sample transport. If your business requires specialist support with biological sample storage or transport of biological samples and regulations, find out about our biobanking solutions today./

Biological research is forward-looking by nature, and the management of samples should reflect that same long-term perspective. Sustainability of biological sample management is becoming a priority for laboratories across the globe. Energy-efficient freezers reduce operational costs as well as environmental impact. Shared facilities for biobanking minimise duplicated infrastructure while also guaranteeing controlled storage conditions. Packaging is another area where improvement can be made, as reusable or recyclable packaging is chosen wherever safety is not compromised. These actions guarantee that the activity of scientific research is compatible with overall environmental goals, so that laboratory routine also contributes to long-term sustainability.
How Restore Harrow Green adds value
While best practices exist throughout the nation, it is costly and challenging to execute them consistently. Restore Harrow Green benefits from delivering:
- ADR-certified drivers with the ability to transport regulated products safely and compliantly.
- An independent temperature-controlled fleet featuring live monitoring technology.
- Bio-storage facilities that are secure from ambient to cryogenic environments.
- End-to-end chain-of-custody documentation for full visibility.
- Rapid recovery and contingency solutions designed to meet time-sensitive or emergency moves.
By combining logistical precision with scientific understanding, we offer biological sample shipping services that guarantee material and data integrity.

Biological sample transport is not merely a technical process, it is a responsibility built on trust. Scientists, clinicians, and institutions depend on safe delivery and uncompromised specimen storage of invaluable materials.
By integrating best practices for lab sample storage, packaging, cold chain handling, and compliance, the risk of shipping lab specimens can be significantly reduced. At Restore Harrow Green, we do more than claim to be a logistics provider. We are an honoured research continuity partner, helping laboratories of all sizes protect their most valuable resources.
If your business requires specialist support with biological sample storage or transport of biological samples and regulations, contact Restore Harrow Green today.
Contact Us Customer Login
Customer Login