Understanding e-recycling begins with recognising its role in responsible business practice. Organisations are increasingly accountable for how they dispose of outdated devices.
The answer is simple: rather than simply pointing to the rise in global e-waste, the focus should be on how businesses can take proactive steps to manage their redundant equipment safely, sustainably, and in line with best practice. By approaching e-recycling strategically, companies can not only reduce risk but also unlock opportunities for efficiency, resource recovery and environmental responsibility.
For businesses, this means partnering with a professional provider such as Restore Datashred who offer key recycling services under the sub-brand Restore Recycle. Ensure devices are securely collected, processed, and either repurposed or broken down according to industry best practice.

What is E-Recycling?
E-recycling involves the recovery, re-use, or responsible destruction of old electronic equipment to prevent harm to the environment and guard sensitive data. It typically involves the collection, disassembly, and reclaiming of materials from computers, smartphones, servers, printers, and hard drives, among other devices, at the end of their life cycle. When done properly, e-recycling allows businesses to maximise value by extracting recoverable components, while also taking away risks associated with data security and environmental impact.
The benefits of responsible e-waste recycling extend far beyond mere compliance. It underpins data protection and reduces waste-to-landfill, while enabling resource efficiency by making key minerals accessible for re-use. Thereafter, those organisations that can create strong control over their e-waste present themselves as responsible, efficient, and future-ready. E-recycling is not just a reactive measure, but a strategic opportunity.
Why is E-Waste Harmful to the Environment?
A lot of people do not know that electronic waste is among the fastest-growing waste types across the globe. As e-waste consists of a combination of hazardous substances like lead, mercury, cadmium, and beryllium, these toxic materials linger quietly in our gadgets until they end up in a landfill, in water, or oxidised. Once this happens, they migrate to soil, groundwater, and then into the environment at large.
This is an ongoing, international issue. Every year, millions of tons of e-waste are produced, but only a fraction of that e-waste is recycled in a safe manner. The rest is commonly exported to other countries, which may be processed by people who lack adequate protective gear, including children. E-waste recycling prevents environmental contamination, protects communities, and keeps reusable materials in circulation

Why is E-Waste Important?
E-waste can be very rich in precious resources such as gold, copper, silver, cobalt, aluminium, as well as other vital minerals. The worth of the metals in isolation is staggering. The value of the global e-waste that is not recycled in 2019 is estimated to be $57 billion. At the same time, lithium and CoBalt demand are reaching unprecedented highs because of electric car battery manufacturing. That’s why e-recycling is also known as “urban mining”, because instead of digging up metals from mines, we extract them from old devices.
And then, of course, there is compliance. Data regulation, such as GDPR, requires that organisations do everything in their power to protect confidential data. That’s including secure destruction of data when devices reach the end of life. This is particularly relevant to e-waste, as end-of-life devices often still contain recoverable information. Ensuring secure destruction through a specialist disposal method of e-waste is therefore not only an environmental responsibility but also a legal requirement to prevent data breaches when hardware is decommissioned.
Why is It Important for Businesses to Recycle E-Waste?
Data Security: Many end-of-life computers, laptops, and drives can still contain data that can be recovered. If not destroyed securely, organisations run the risk of inappropriate exposure of data. Using accredited providers of destruction reduces this risk and ensures full compliance.
Cost Efficiency: Effective asset disposal optimises storage capacity, simplifies inventory management, and prevents potential penalties associated with improper waste handling. Approached from a strategic perspective, e-waste management could help support operational efficiency and long-term cost savings.
Environmentally Responsible: Modern supply chains today put a lot of emphasis on sustainability. Businesses are consequently supposed to show responsible disposal practices, where the recycling of electronic equipment should be carried out in a manner that avoids harming the environment and supports broader sustainability outcomes.
Regulatory compliance: A company needs to prove legal destruction of confidential media, for which a Certificate of Destruction is sometimes required.
Restore Datashred, a provider of data destruction services, supports all of these priorities by ensuring responsible IT asset destruction, giving customers confidence that devices have been disposed of responsibly, meaning confidential data is forever irrecoverable.
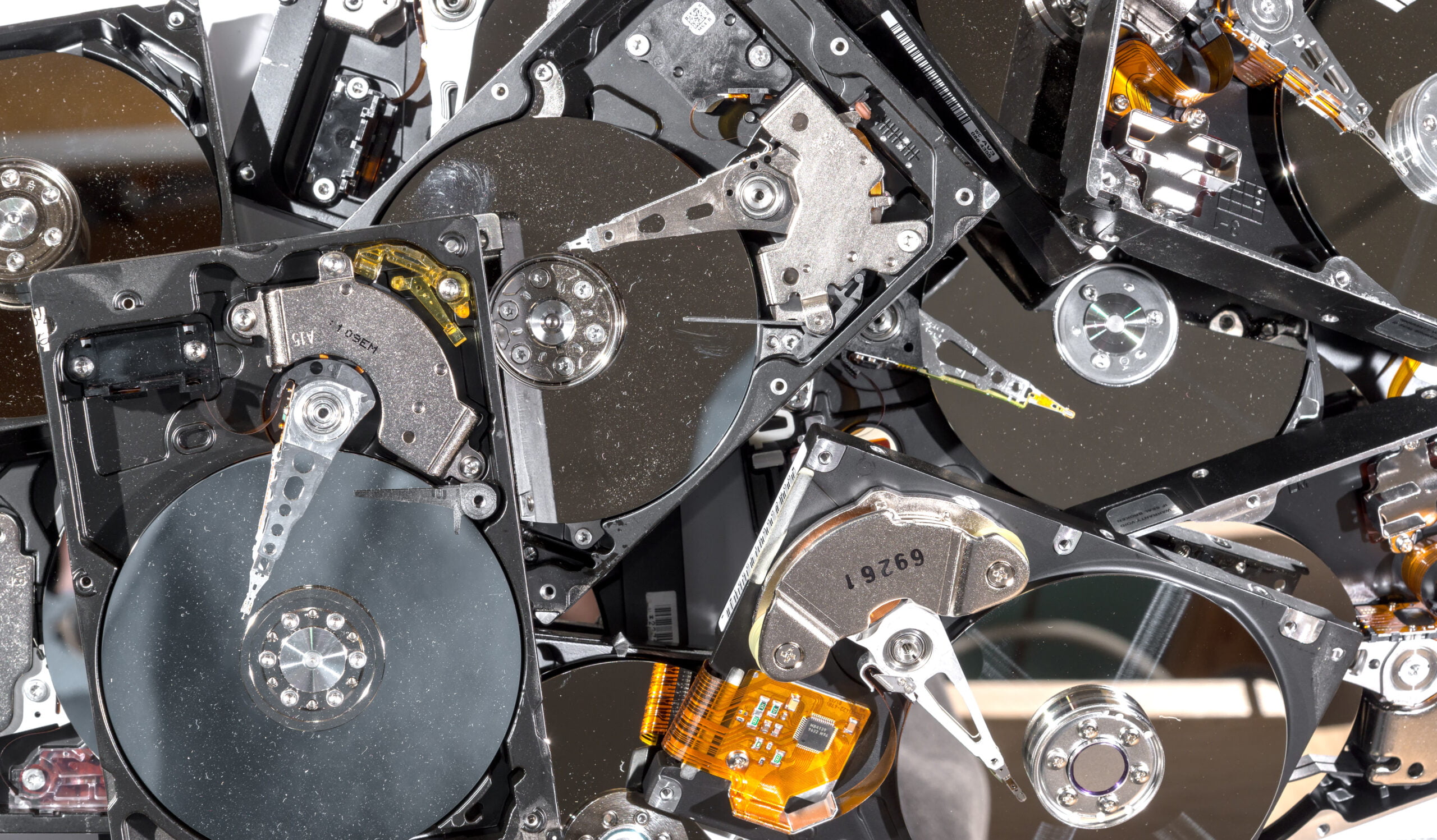
Why E-Waste Recycling is Important to the United Kingdom
Given that the UK is amongst the highest producers of e-waste in Europe, responsible e-waste disposal has never been more imperative. Professional services work to make sure that harmful materials do not find their way into the environment, as well as to maintain reusable materials in circulation, which is an important component of sustainability for this nation.
Ways to Recycle E-Waste
There are several methods of e-waste recycling, which vary according to whether they’re for business or for individuals, including:
Manufacturer Take-Back Schemes
Many brands, such as Apple and Samsung, have programs where you can return old devices for recycling when you purchase a new one.

Professional IT Recycling Services
Ideal for organisations handling confidential or sensitive data. These providers manage devices securely from collection through to final recycling or destruction.

Donation or Reuse
Devices are refurbished and provided to charities, schools or community initiatives, helping to reduce waste while supporting social value projects.

Best Methods for E-Waste Management
Effective tech disposal involves choosing the right methods of e-waste management, including:
- Asset tracking and inventory management – Knowing what needs destroying.
- Secure transportation of collection – GPS-enabled vehicles, screened staff.
- Certified data destruction – Services include physical shredding of computer drives.
- Recycling of materials responsibly – Nothing harmful enters landfills.
Restore Datashred’s service is designed this way, with ease of use for companies to undertake all stages of this process.
Here’s what happens to e-waste when it is recycled:
The initial step in e-waste disposal processes adopted by reputable companies is secure collection. Devices are collected from the business premises at an arranged date and time, using GPS-located vehicles, which are recorded in an asset register. This also prevents what is perhaps the biggest risk: devices that have not been properly managed going out of the office without a clear chain of custody.

Before shredding any material, the equipment is sorted carefully. Functional parts for possible reuse are separated from harmful material at this point. This is an important stage as items like toner, batteries, and capacitors are all contaminants, as well as potential explosion devices if shredded early.

For data-containing assets such as hard drives, shredding is the standard by which everything else is measured for destroying data irretrievably. Restore Datashred is an expert in this area, employing high-security shredding machinery which reduces drives to particles in line with BS EN 15713 standards. This is how e-waste is recycled at the most noticeable level of processing: it is sorted into small, indecipherable pieces.

The shredded material is then further processed to reclaim usable metals. Ferromagnetic metals like steel and iron are removed by strong magnetic attraction, which results in reduced waste.

Recycling plants use induced electric currents to separate aluminium as well as other non-ferrous metals from waste material. This process converts waste into valuable material for recycling.

Light plastics float, whereas glass and heavier materials sink, which is perhaps the most basic but most efficient principle of secondary separation. At this point in the e-waste recycling process, the material is ready to be recycled for further use in products.

Once destruction is finished, companies get a certificate of destruction, which is an important requirement for satisfying GDPR compliance as well as internal audits. This transparency is an essential component of the e-waste disposal process from a corporate compliance standpoint.

The final step provides an answer to what happens to e-waste when it is recycled. Reusable materials from metals find suitable applications in manufacturing, plastics get recycled, and toxic waste is handled properly.
What is E-Waste and Recycling Trying to Solve?
While the increasing focus on e-waste and recycling is more than just a matter of environmental awareness, it also reflects a shift in how we consume technologies. It can lead to the contamination of ecosystems, organisations exposed to data breaches can result in regulatory penalties, and even raise demand for destructive mining.
Appropriate recycling methods, however, work in the reverse. They protect the environment, which is vital, and help maintain data security by ensuring that any data stored is destroyed.
A Safer, More Sustainable Way Forward
The question is not whether the world needs better e-waste management practices; it’s how quickly this is possible. Safe, accredited, and trustworthy companies, such as Restore Datashred, enable organisations to easily behave responsibly, protect themselves, as well as minimise their negative environmental influence in a structured, safe, and compliant manner.
Contact Us Customer Login
Customer Login


